Ionizing Photon Production Efficiencies and Chemical Abundances at Cosmic Dawn Revealed by Ultra-Deep Rest-Frame Optical Spectroscopy of JADES-GS-z14-0
Ionizing Photon Production Efficiencies and Chemical Abundances at Cosmic Dawn Revealed by Ultra-Deep Rest-Frame Optical Spectroscopy of JADES-GS-z14-0
Dec 23, 2025· ,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
Jakob M. Helton
Jane E. Morrison
Kevin N. Hainline
Francesco D'Eugenio
George H. Rieke
Stacey Alberts
Stefano Carniani
Joel Leja
Yijia Li
Pierluigi Rinaldi
Jan Scholtz
Meredith Stone
Christopher N. A. Willmer
Zihao Wu
William M. Baker
Andrew J. Bunker
Stephane Charlot
Jacopo Chevallard
Nikko J. Cleri
Emma Curtis-Lake
Eiichi Egami
Daniel J. Eisenstein
Peter Jakobsen
Zhiyuan Ji
Benjamin D. Johnson
Nimisha Kumari
Xiaojing Lin
Jianwei Lyu
Roberto Maiolino
Michael Maseda
Pablo G. Pérez-González
Marcia J. Rieke
Brant Robertson
Aayush Saxena
Fengwu Sun
Sandro Tacchella
Hannah Ubler
Giacomo Venturi
Christina C. Williams
Chris Willott
Joris Witstok
Yongda Zhu
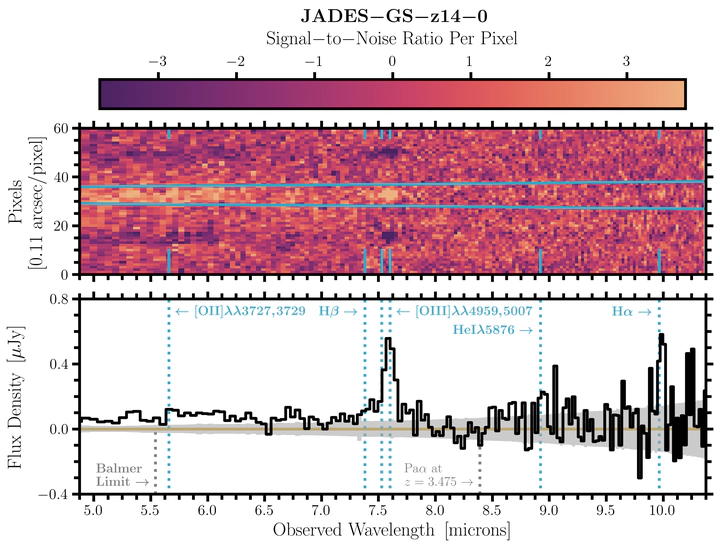 Figure 2 from Helton et al. (2025, ApJL, submitted).
Figure 2 from Helton et al. (2025, ApJL, submitted).Abstract
JWST has discovered an early period of galaxy formation that was more vigorous than expected, which has challenged our understanding of the early Universe. In this work, we present the longest spectroscopic integration ever acquired by JWST/MIRI ($t_{\mathrm{obs}} \approx 34\ \mathrm{hr}$
). This spectrum covers the brightest rest-frame optical nebular emission lines for the luminous galaxy JADES-GS-z14-0 at $z > 14$
. Most notably, we detect $[\mathrm{OIII}] \lambda\lambda 4959{,}5007$
at $\approx 11 \sigma$
and $\mathrm{H}\alpha$
at $\approx 4 \sigma$
with these ultra-deep observations. These lines reveal that JADES-GS-z14-0 has low dust attenuation with a recent star-formation rate of $\mathrm{SFR} \approx 10 \pm 2\ M_{\odot} / \mathrm{yr}$
, star-formation rate surface density of $\Sigma_{\mathrm{SFR}} \approx 23 \pm 5\ M_{\odot}/\mathrm{yr}/\mathrm{kpc}^{2}$
, and ionizing photon production efficiency of $\xi_{\mathrm{ion}} \approx 10^{25.3 \pm 0.1}\ \mathrm{Hz/erg}$
. Using standard strong-line diagnostics, we infer a gas-phase oxygen abundance of $\mathrm{log}_{10}(\mathrm{O/H}) + 12 \approx 7.6 \pm 0.4$
($\approx 10\%\ Z_{\odot}$
), carbon-to-oxygen ratio of $[\mathrm{C/O}] \approx -0.4 \pm 0.4$
, ionization parameter of $\mathrm{log}_{10}(U) \gtrsim -2.4$
, and density of $n_{\mathrm{H}} \approx 720 \pm 210\ \mathrm{cm}^{-3}$
. Using detailed photoionization modeling, we instead derive $\mathrm{log}_{10}(\mathrm{O/H}) + 12 \approx 8.4_{-0.4}^{+0.4}$
($\approx 50\%\ Z_{\odot}$
), $\mathrm{log}_{10}(U) \approx -1.5_{-0.4}^{+0.3}$
, and $n_{\mathrm{H}} \approx 520_{-310}^{+480}\ \mathrm{cm}^{-3}$
. The inferred properties of JADES-GS-z14-0 are similar to those measured for similarly luminous galaxies at $z > 10$
with previous MIRI/Spectroscopy, such as GHZ2/GLASSz12, GN-z11, and MACS0647-JD1. These results suggest extreme ionization conditions and rapid metal enrichment less than $300$
million years after the Big Bang. Existing simulations are unable to reproduce the empirical and inferred properties of JADES-GS-z14-0. The spectrum that we obtained with the MIRI/LRS includes a tentative detection of the rarely seen $\mathrm{HeI} \lambda 5876$
line, indicating possible contributions from shocked nebular gas. This work demonstrates an important step toward understanding the formation of the first stars and heavy elements in the Universe.
Type
Publication
eprint arXiv:2512.19695
High-Redshift Galaxies
Galaxy Formation
Galaxy Evolution
Chemical Abundances
Infrared Spectroscopy
Emission Line Galaxies
Related
- SMILES: Potentially Higher Ionizing Photon Production Efficiency in Overdense Regions
- Not Just a Dot: The Complex UV Morphology and Underlying Properties of Little Red Dots
- The z > 9 Galaxy UV Luminosity Function from the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey: Insights into Early Galaxy Evolution and Reionization
- The Stellar Populations and Rest-Frame Colors of Star-Forming Galaxies at z = 8: Exploring the Impact of Filter Choice and Star Formation History Assumption with JADES
- The eventful life of a luminous galaxy at z = 14: metal enrichment, feedback, and low gas fraction?